Terminology
Terminology explains all the terms used in the financial world in a simple language such as Investments, Insurance, Concept, Ideas and new words
Types of Debt funds & Hybrid mutual funds
Debt mutual funds invest in fixed income securities like bonds while hybrid mutual funds invest in both equity and debt securities Different types of Debt…
Different types of Equity funds
A mutual fund scheme that invests primarily in company shares or stocks is known as an equity fund. Growth funds are another name for them.…
What is a Stock Exchange?
A stock exchange is a place where investors can purchase publicly traded companies' shares or sell them. It's comparable to a shopping mall for stock. From one…
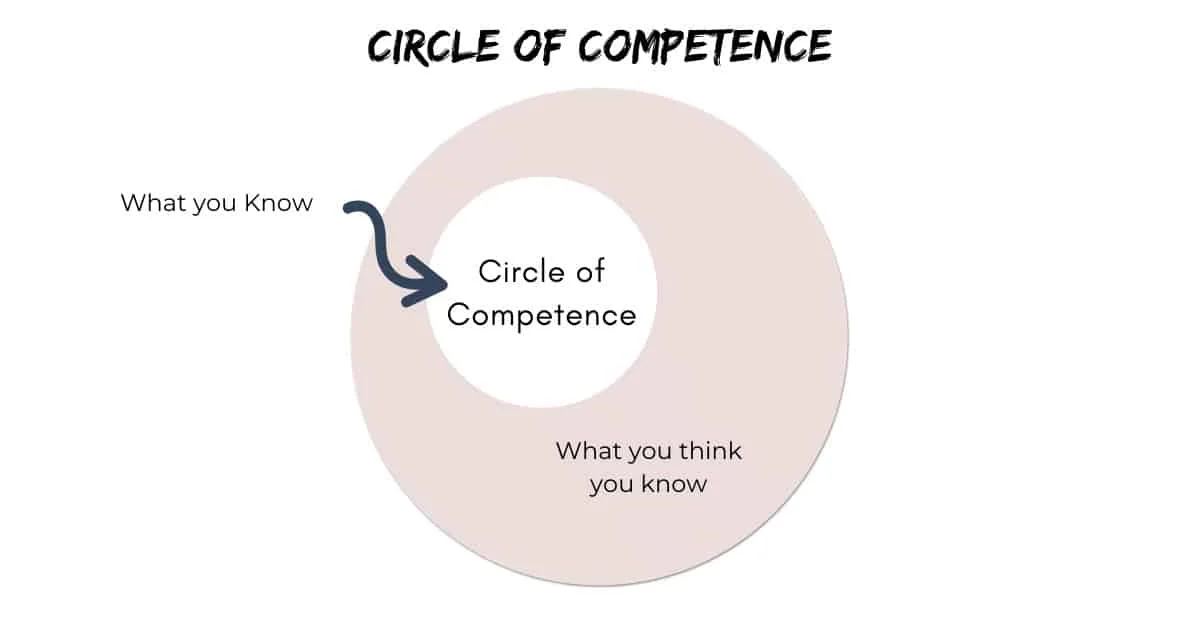
Understanding what is the circle of competence?
Anything that falls within your skill set, knowledge, or experience is considered to be within your Circle of competence. Amazon is really good at one…
Bear and Bull Market
A 'bear market' is a situation in which stock prices drop from a recent peak by more than 20%. When the stock price grows by…
Stories
What is Gini Coefficient or Gini index
The Gini coefficient, often known as the Gini index, is a statistic that measures the…
What is the Multi Commodity Exchange (MCX)?
The Multi Commodities Exchange of India (MCXI) is a government-owned commodity exchange in India. It…
Price Elasticity
The term "price elasticity" describes the relationship between demand and the cost of a product…
Unlimited Company
The proprietors of an unlimited corporation may be held entirely accountable for the company's debt.…
Pairs Trade
The stocks of many different companies have a tendency to react in the same way…
Operating lease
In the case of an operating lease, the lessor retains ownership of the items rented…